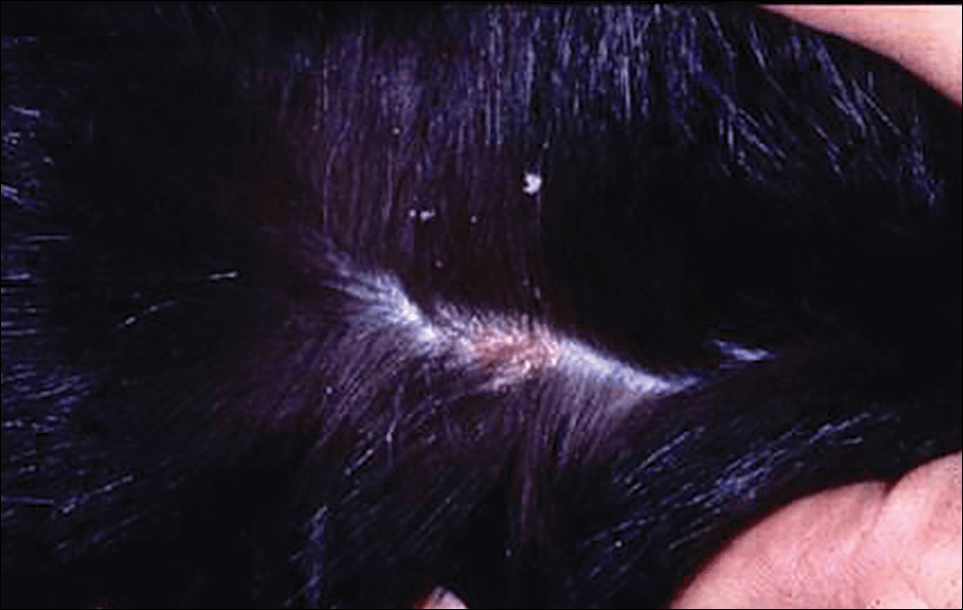
Cheyletiellosis humans, also known as walking dandruff, is a skin condition caused by the infestation of a tiny mite called Cheyletiella yasguri. This mite is typically found on animals, such as cats and rabbits, but can also infest humans who come into close contact with infected animals.
The symptoms of cheyletiellosis humans can include intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin. In some cases, the infestation can also lead to hair loss. The mites are most commonly found on the scalp, but can also infest other areas of the body, such as the arms, legs, and trunk.
Cheyletiellosis humans is diagnosed by a doctor or dermatologist who will examine the skin and look for the presence of the mites. Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites. In some cases, oral medications may also be prescribed.
Cheyletiellosis Humans
Cheyletiellosis humans, also known as walking dandruff, is a skin condition caused by the infestation of a tiny mite called Cheyletiella yasguri. This mite is typically found on animals, such as cats and rabbits, but can also infest humans who come into close contact with infected animals.
- Cause: Cheyletiellosis humans is caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can include intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin.
- Diagnosis: Cheyletiellosis humans is diagnosed by a doctor or dermatologist who will examine the skin and look for the presence of the mites.
- Treatment: Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites.
- Prevention: Cheyletiellosis humans can be prevented by avoiding contact with infected animals.
- Prevalence: Cheyletiellosis humans is a relatively rare condition.
- Complications: In some cases, cheyletiellosis humans can lead to hair loss.
- History: Cheyletiellosis humans was first described in the 19th century.
- Research: There is ongoing research into the development of new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis humans.
- Outlook: Cheyletiellosis humans is a treatable condition with a good prognosis.
Cheyletiellosis humans is a skin condition that can be caused by contact with infected animals. Symptoms can include intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin. Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications to kill the mites. Cheyletiellosis humans is a relatively rare condition, but it can be prevented by avoiding contact with infected animals.
Cause
Cheyletiellosis humans is a skin condition that is caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite. This mite is typically found on animals, such as cats and rabbits, but can also infest humans who come into close contact with infected animals. The mites can cause intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin.
In order to understand cheyletiellosis humans, it is important to understand the cause of the condition. The Cheyletiella yasguri mite is a small, parasitic mite that lives on the skin of animals. The mites feed on the skin cells and body fluids of their host. When the mites infest humans, they can cause a variety of symptoms, including itching, redness, and scaling of the skin. In some cases, the mites can also lead to hair loss.
Understanding the cause of cheyletiellosis humans is important for preventing and treating the condition. By avoiding contact with infected animals, humans can reduce their risk of developing cheyletiellosis humans. If someone does develop cheyletiellosis humans, it is important to seek treatment from a doctor or dermatologist. Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cheyletiellosis humans are directly related to the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite. These mites burrow into the skin and feed on the skin cells and body fluids of their host. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Intense itching: The mites can cause intense itching, which can be especially bothersome at night.
- Redness: The skin can become red and inflamed due to the irritation caused by the mites.
- Scaling: The skin can become dry and scaly due to the damage caused by the mites.
These symptoms can be very uncomfortable and can interfere with daily life. In some cases, the infestation can also lead to hair loss. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor or dermatologist to get a diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis
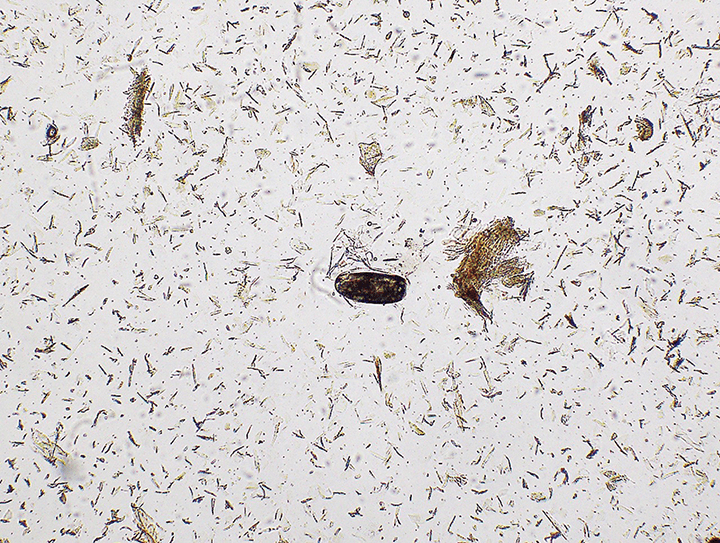
A proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of cheyletiellosis humans. The diagnosis is typically made by a doctor or dermatologist who will examine the skin and look for the presence of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite. The mites are small and white, and they can be difficult to see with the naked eye. However, a doctor or dermatologist can use a microscope to magnify the skin and look for the mites.
In some cases, a doctor or dermatologist may also order a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. A skin biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin and examining it under a microscope. This can help to rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
An accurate diagnosis is important for getting the right treatment for cheyletiellosis humans. Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites. In some cases, oral medications may also be prescribed.
Treatment
Cheyletiellosis humans is a skin condition that can be caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite. Symptoms can include intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin. Treatment typically involves the use of topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites.
Topical medications are applied directly to the skin and work by killing the mites on contact. They are typically used for mild to moderate cases of cheyletiellosis humans. In some cases, oral medications may also be prescribed for more severe infestations.
It is important to follow the doctor's instructions carefully when using topical medications for cheyletiellosis humans. The medications should be applied to the affected areas of skin as directed and for the length of time prescribed. It is also important to avoid contact with the eyes and mouth when using topical medications.
Treatment for cheyletiellosis humans is typically successful if the instructions are followed carefully. However, it is important to note that re-infestation can occur if the source of the infestation is not identified and treated. Therefore, it is important to treat all animals that have been in contact with the infested person.
Prevention
Cheyletiellosis humans is a skin condition caused by infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite, which typically affects animals such as cats and rabbits. Understanding the connection between prevention and cheyletiellosis humans is crucial for effective management of the condition.
Avoiding contact with infected animals is a primary preventive measure for cheyletiellosis humans. Infected animals, particularly cats and rabbits, carry the mites that can transmit the infestation to humans through direct contact. By limiting exposure to these animals or implementing proper hygiene practices when interacting with them, the risk of acquiring cheyletiellosis humans can be significantly reduced.
Furthermore, maintaining a clean environment and regularly disinfecting areas where animals reside can help prevent the spread of the mites. Regular veterinary check-ups for pets and prompt treatment of any skin conditions they may develop can also help control the mite population and prevent transmission to humans.
In conclusion, understanding the link between prevention and cheyletiellosis humans highlights the importance of avoiding contact with infected animals and implementing proper hygiene practices. These preventive measures are essential for reducing the risk of infestation and maintaining good skin health.
Prevalence
The prevalence of cheyletiellosis humans, a skin condition caused by the Cheyletiella yasguri mite, plays a significant role in understanding the nature and impact of this condition. Its relatively rare occurrence has several implications and is intricately connected to various aspects of cheyletiellosis humans.
One crucial implication is that the rarity of cheyletiellosis humans contributes to its under-recognition and potential misdiagnosis. Due to its infrequency, healthcare providers may not readily consider cheyletiellosis humans when presented with patients exhibiting suggestive symptoms. Consequently, accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment may be delayed, leading to prolonged discomfort and potential complications for affected individuals.
Furthermore, the rarity of cheyletiellosis humans influences the allocation of research resources and the development of targeted interventions. Limited prevalence can hinder the prioritization of research efforts dedicated to understanding the complexities of the condition, exploring novel treatment modalities, and implementing effective prevention strategies.
Despite its relatively low prevalence, cheyletiellosis humans remains a legitimate concern, particularly for individuals who are in close contact with animals, such as veterinarians, animal handlers, and pet owners. Understanding the prevalence of cheyletiellosis humans is essential for raising awareness among healthcare professionals and the general public, promoting early detection, and facilitating prompt management to prevent further spread and complications.
Complications
Cheyletiellosis humans, a skin condition caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite, can lead to a range of complications, including hair loss. Understanding the connection between cheyletiellosis humans and hair loss is crucial for effective management and prevention of this condition.
- Inflammation and Damage to Hair Follicles
The Cheyletiella yasguri mite feeds on skin cells and body fluids, causing intense itching and irritation. This inflammation can extend to the hair follicles, damaging them and disrupting the normal hair growth cycle. As the inflammation persists, hair follicles can become weakened, leading to hair loss.
- Mechanical Damage from Scratching
The intense itching associated with cheyletiellosis humans often leads to excessive scratching. This mechanical damage can further injure the hair follicles and surrounding skin, contributing to hair loss.
- Secondary Bacterial Infections
The open wounds caused by scratching can provide an entry point for bacteria, leading to secondary infections. These infections can further damage the hair follicles and hinder hair growth.
- Nutritional Deficiencies
In severe cases of cheyletiellosis humans, the mites can consume a significant amount of skin cells and body fluids, leading to nutritional deficiencies. This can affect the overall health of the hair and contribute to hair loss.
The connection between cheyletiellosis humans and hair loss highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Prompt management of the infestation can reduce the risk of hair loss and other associated complications, ensuring better outcomes for affected individuals.
History
The historical context of cheyletiellosis humans, first described in the 19th century, sheds light on the evolution of our understanding of this skin condition and its implications for modern medicine.
- Recognition and Classification
The initial description of cheyletiellosis humans in the 19th century marked a significant milestone in recognizing and classifying the condition. This laid the foundation for subsequent research, leading to a better understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment.
- Evolution of Treatment Approaches
The historical record provides insights into the evolution of treatment approaches for cheyletiellosis humans. Early treatments were likely based on empirical observations and anecdotal evidence, but over time, more scientific and effective therapies were developed.
- Changing Prevalence and Distribution
Historical data can help us understand changes in the prevalence and distribution of cheyletiellosis humans over time. Factors such as improved hygiene practices, advancements in veterinary medicine, and changes in human-animal interactions may have influenced the epidemiology of the condition.
- Influence on Current Management
An understanding of the history of cheyletiellosis humans informs current management strategies. By learning from past experiences and successes, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures.
Exploring the historical context of cheyletiellosis humans provides valuable insights into the nature and evolution of this condition. It enhances our understanding of its clinical presentation, treatment approaches, and broader implications for human health.
Research
The ongoing research into the development of new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis humans plays a pivotal role in the understanding, management, and prevention of this skin condition. This research is driven by the need to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes.
Cheyletiellosis humans, caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite, can lead to a range of symptoms, including intense itching, redness, scaling, and in severe cases, hair loss. Current treatment options, such as topical medications and oral medications, aim to eliminate the mites and alleviate symptoms. However, limitations associated with existing treatments, such as potential side effects, resistance development, and incomplete eradication of the mites, necessitate the exploration of new and more effective approaches.
Research efforts are focused on identifying novel therapeutic targets, developing more potent and selective drugs, and exploring alternative treatment modalities. This includes investigating the use of different drug delivery systems, such as nanotechnology, to enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects. Additionally, research is directed towards understanding the underlying mechanisms of cheyletiellosis humans, including the host-parasite interactions and the immune response, to inform the development of more targeted therapies.
The development of new and more effective treatments for cheyletiellosis humans is crucial for improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Successful research outcomes have the potential to transform the treatment landscape, leading to better patient outcomes, reduced disease burden, and improved public health.
Outlook
Cheyletiellosis humans is a treatable condition with a good prognosis, meaning that most people who develop this condition can expect to make a full recovery. The prognosis is generally good because the condition is treatable with topical medications that are effective at eliminating the mites that cause the infestation. Additionally, cheyletiellosis humans is not a serious condition and does not typically lead to any long-term health problems.
The key to a good prognosis is early diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, cheyletiellosis humans can lead to more severe symptoms, such as hair loss and secondary skin infections. However, with early diagnosis and treatment, most people can expect to make a full recovery without any complications.
The outlook for cheyletiellosis humans is also good because the condition is not contagious to other humans. This means that people who have cheyletiellosis humans do not need to worry about spreading the condition to their family members or friends.
Overall, the outlook for cheyletiellosis humans is good. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people can expect to make a full recovery without any complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cheyletiellosis Humans
Cheyletiellosis humans, also known as walking dandruff, is a skin condition caused by the infestation of a tiny mite called Cheyletiella yasguri. This mite is typically found on animals, such as cats and rabbits, but can also infest humans who come into close contact with infected animals.
Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions about cheyletiellosis humans:
Question 1: What are the symptoms of cheyletiellosis humans?The most common symptoms of cheyletiellosis humans are intense itching, redness, and scaling of the skin. In some cases, the infestation can also lead to hair loss.
Question 2: How is cheyletiellosis humans diagnosed?Cheyletiellosis humans is diagnosed by a doctor or dermatologist who will examine the skin and look for the presence of the mites. In some cases, a skin biopsy may also be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Question 3: How is cheyletiellosis humans treated?Cheyletiellosis humans is typically treated with topical medications, such as permethrin or malathion, to kill the mites. In some cases, oral medications may also be prescribed.
Question 4: How can cheyletiellosis humans be prevented?Cheyletiellosis humans can be prevented by avoiding contact with infected animals. If you do come into contact with an infected animal, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
Question 5: Is cheyletiellosis humans contagious?Cheyletiellosis humans is not contagious to other humans. However, it is important to treat all animals that have been in contact with the infested person to prevent re-infestation.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for cheyletiellosis humans?The prognosis for cheyletiellosis humans is good. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people can expect to make a full recovery without any complications.
If you have any concerns about cheyletiellosis humans, please speak to your doctor or dermatologist.
Next:
Learn more about the causes of cheyletiellosis humans.
Tips for Managing Cheyletiellosis Humans
Cheyletiellosis humans, also known as walking dandruff, is a skin condition caused by the infestation of a tiny mite called Cheyletiella yasguri. This mite is typically found on animals, such as cats and rabbits, but can also infest humans who come into close contact with infected animals.
If you have been diagnosed with cheyletiellosis humans, there are a few things you can do to manage the condition and prevent its spread:
Tip 1: Follow your doctor's instructions carefully.
Your doctor will prescribe a topical medication to kill the mites. It is important to follow the instructions carefully and to use the medication for the full length of time prescribed.
Tip 2: Wash your bedding and clothing in hot water.
The mites can live on bedding and clothing, so it is important to wash these items in hot water to kill the mites.
Tip 3: Vacuum your home thoroughly.
The mites can also live in carpets and furniture, so it is important to vacuum your home thoroughly to remove the mites.
Tip 4: Treat your pets.
If you have pets, it is important to treat them for cheyletiellosis as well. This will help to prevent the mites from re-infesting you.
Tip 5: Avoid contact with infected animals.
Once you have been treated for cheyletiellosis humans, it is important to avoid contact with infected animals to prevent re-infestation.
By following these tips, you can help to manage cheyletiellosis humans and prevent its spread.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- Following your doctor's instructions can help ensure effective treatment.
- Washing bedding and clothing in hot water and vacuuming regularly can eliminate mites from your environment.
- Treating pets and avoiding contact with infected animals can prevent re-infestation.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
Cheyletiellosis humans is a treatable condition, but it is important to take steps to manage the condition and prevent its spread.
Conclusion
Cheyletiellosis humans, caused by the infestation of the Cheyletiella yasguri mite, is a skin condition that can cause intense itching, redness, and scaling. The condition is treatable with topical medications, and the prognosis is good. However, it is important to take steps to prevent re-infestation, such as treating pets and avoiding contact with infected animals.
Cheyletiellosis humans is a reminder of the importance of practicing good hygiene and taking precautions when interacting with animals. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to prevent and manage cheyletiellosis humans.
Unveiling The Truth: Melanie Martinez's Breast Implant Mystery
Unveiling "We Bought A Funeral Home" Season 2: Release Date, Families, And Surprises
Unveil The Secrets: Discover The Unique World Of The Weiner Golden Retriever Mix
Guide to Cheyletiellosis Clinician's Brief
Dandruff Mites On Humans Toxoplasmosis My XXX Hot Girl
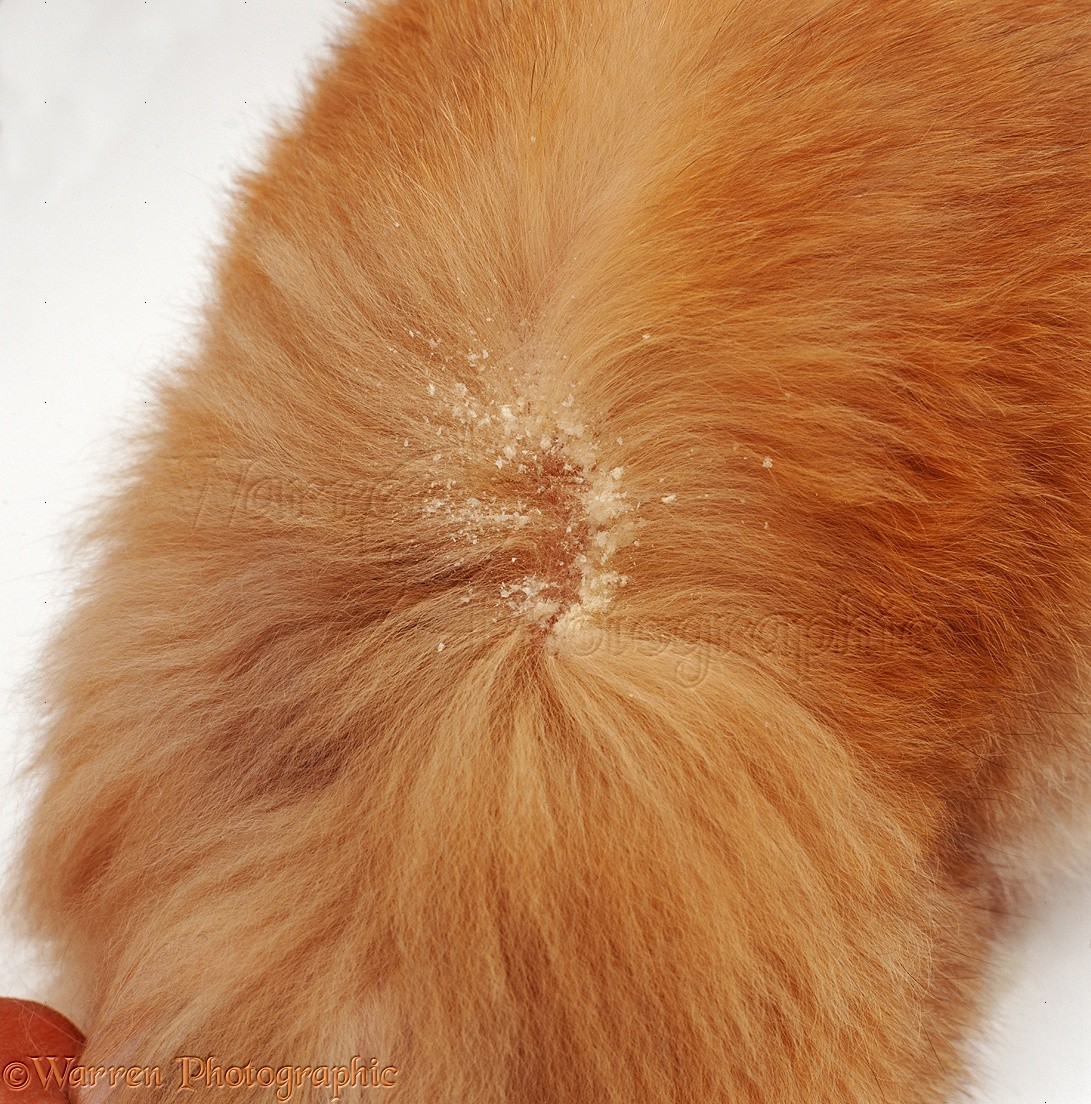

Cheyletiellosis Cat
ncG1vNJzZmijkaKyqX6NmqSsa16Ztqi105qjqJuVlru0vMCcnKxmk6S6cK%2FHnrClnaSesq24zqygrGWYqrqiutJnn62lnA%3D%3D